Origins of the Batagaika “Scar”
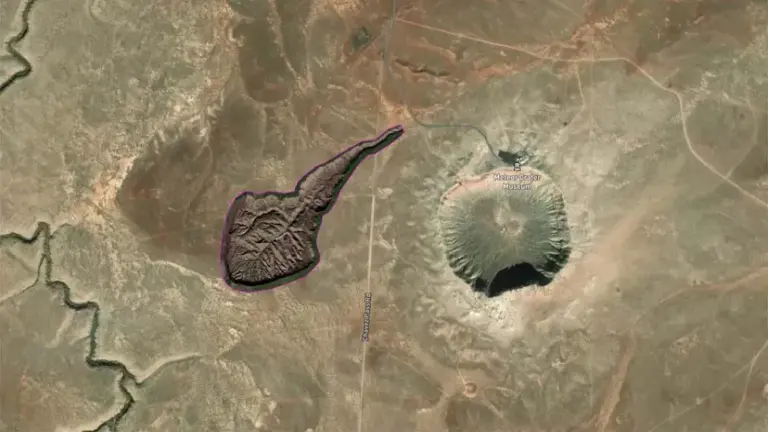
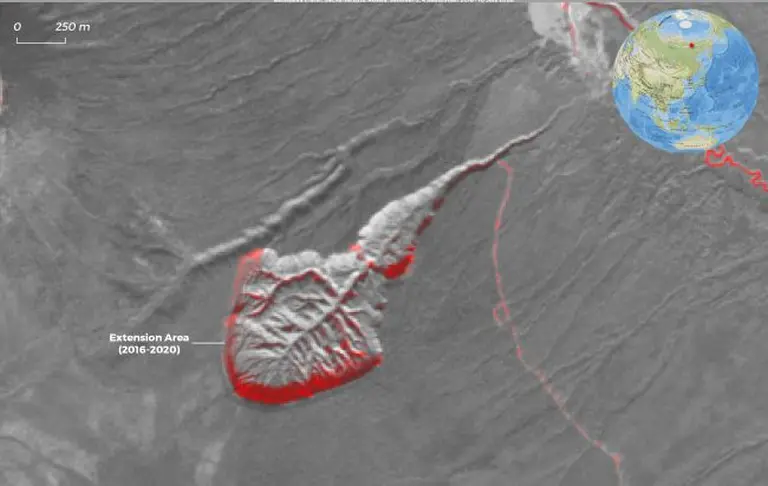
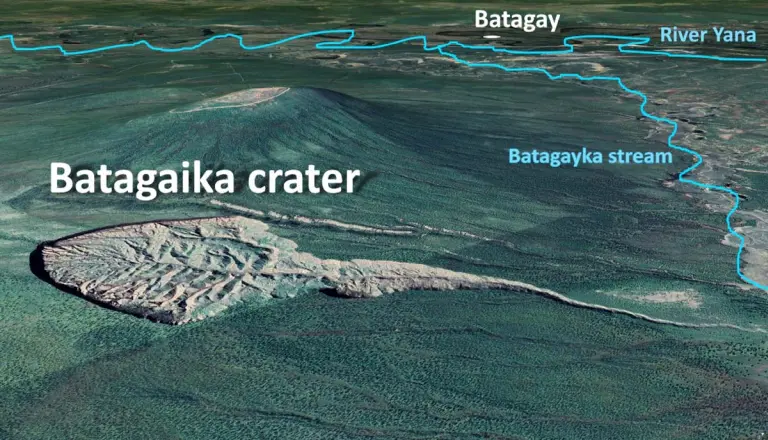
The Batagaika Crater formed in the 1960s after a nearby forest was cleared for road construction. The loss of natural vegetation exposed the underlying permafrost to sunlight and rising temperatures, triggering a process of thawing and collapse known as thermokarst.
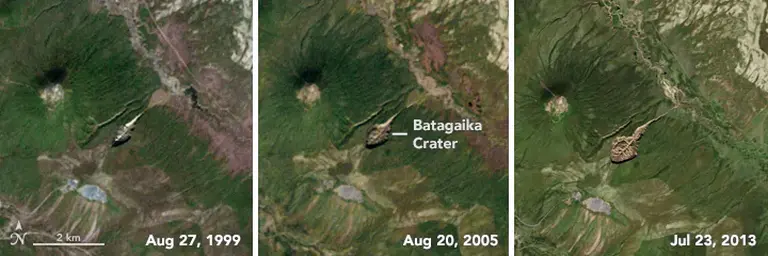
Since then, the crater has been expanding at a rate of 10 to 30 meters per year, depending on temperature and precipitation. The continued thawing of permafrost not only reshapes the landscape but also releases significant amounts of greenhouse gases such as methane and carbon dioxide, exacerbating the vicious cycle of climate change.
A Gateway to the Ancient Past
Beyond being a stark example of climate change, the Batagaika Crater serves as a unique archaeological and biological treasure trove. Exposed permafrost layers along its walls reveal hundreds of thousands of years of climatic, biological, and geological history.
- Fossil treasures: Remains of Ice Age animals such as woolly rhinos, cave lions, steppe bison, and wolves have been uncovered, helping scientists reconstruct ancient ecosystems, from sprawling grasslands to forests of spruce and pine that once covered the region.
- Ancient permafrost: Parts of the permafrost in the crater are estimated to be up to 650,000 years old—the oldest known in Eurasia.
These discoveries hold immense significance for studying historical climate change and predicting future trends.
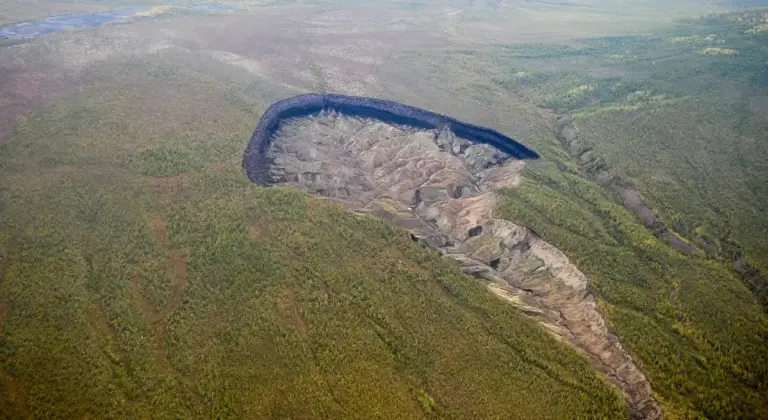

A Global Environmental Challenge
The Batagaika Crater is not just a scar on the landscape but also a symbol of a global challenge: permafrost thawing. Scientists warn that permafrost contains vast amounts of carbon buried over millennia. As the ice melts, these greenhouse gases are released, accelerating global warming.
While the Batagaika Crater stands out for its size and rapid growth, it is just one of thousands of similar sinkholes that have appeared across Siberia in recent years. These phenomena are stark evidence of the Arctic’s rapidly rising temperatures, which are increasing at twice the global average.
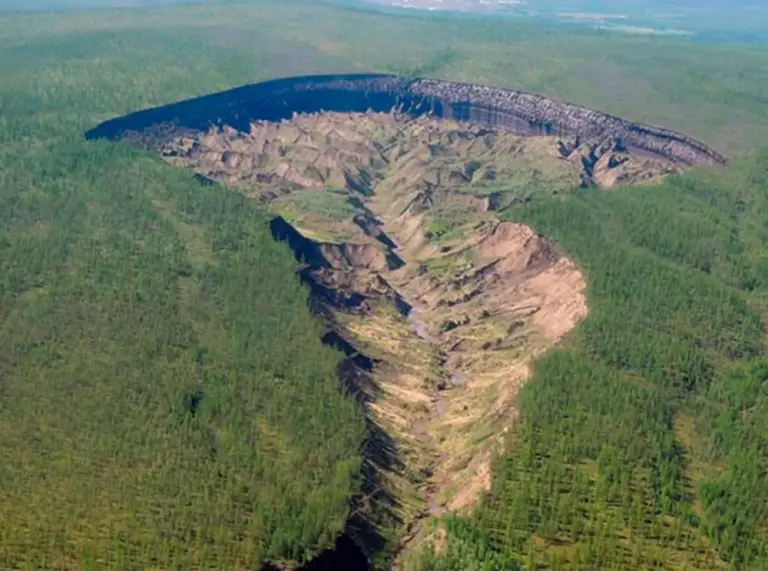

A Surreal Spectacle and a Lesson for Humanity
From above, the Batagaika Crater resembles a massive crack on Earth, both awe-inspiring and terrifying. Explorers have captured stunning images from within its depths, revealing vividly colored sediment layers and shimmering ice walls, like a natural tapestry of time etched into the ground.
The crater is not just a research site but also a serious warning about the consequences of climate change and humanity’s careless interference with natural ecosystems.
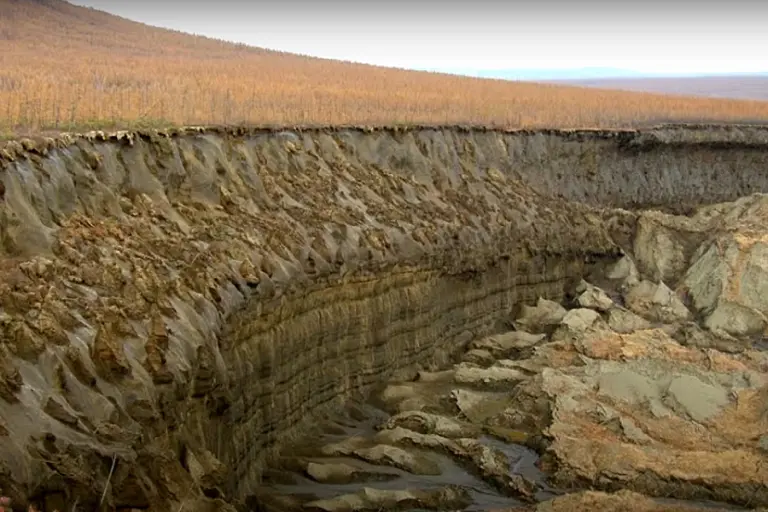


The Future of Batagaika and the Lessons It Offers
The Batagaika Crater continues to expand, and its secrets are still being unraveled. However, its story raises a broader question: What can we do to mitigate the impacts of climate change and protect fragile ecosystems like the Arctic?
The Batagaika Crater is more than a natural landmark—it is a reminder that nature records the passage of time and that we bear responsibility for preventing future “scars” on our planet.